Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a game-changer/step change in the way in which subsurface workflows can be optimised. These state-of-the-art tools are being utilised to understand the suitability of storage sites for use in carbon sequestration projects. Understanding storage capacity, the risk to containment, and the seal capacity are all critical elements affected by the presence of faulting that can be most clearly understood using AI.
Seismic and well data courtesy of the UK National Data Repository (NPR).
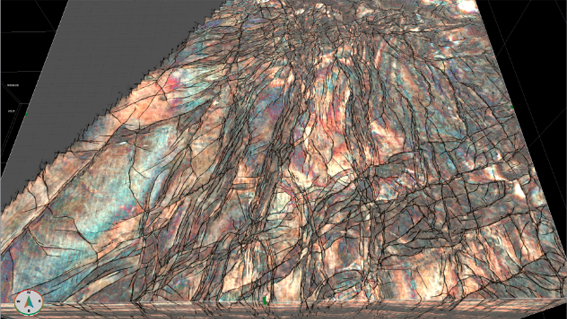
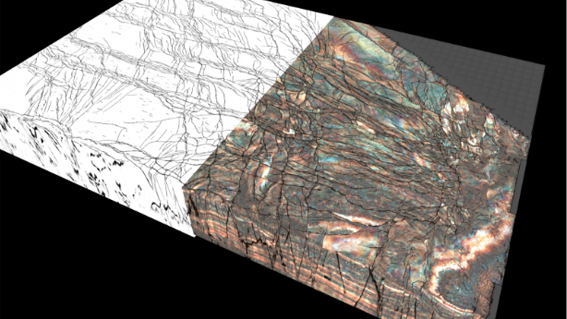
AI can rapidly investigate potential CCUS aquifers sites and surrounding structures for fault presence. Compared to traditional attributes, which can mask fault presence in complex areas, AI can produce a sharp, clear fault response.
Carbon Capture, Utilisation and Storage (CCUS) is thought to be an answer to reduce net CO2 emissions globally. Carbon dioxide sequestration from large power plants or heavy industries from large industrial installations.
The SNS Triassic Bunter Sandstone has been identified by man as an ideal aquifer for CCUS, with several faulted structures (Bunter mounds) potential storage sites.
Identifying appropriate storage sites is essential for successful CO2 storage, with a key parameter focusing on the trap and seal integrity.
Click here to read the case study in full to find out if it is possible to rapidly screen CCUS site locations accurately to de-risk trap and seal integrity using AI networks for fault detection.
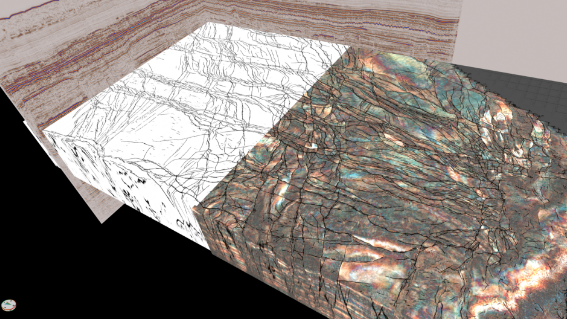
Image Title
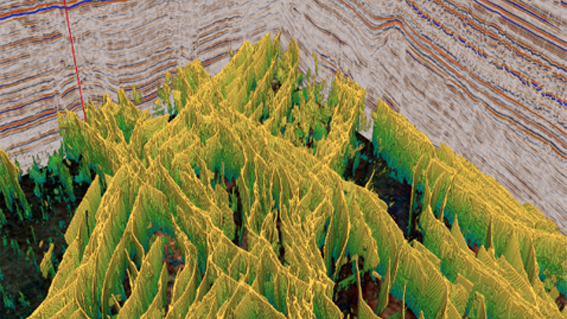
Image Title

Image Title
Title
slider-img-5
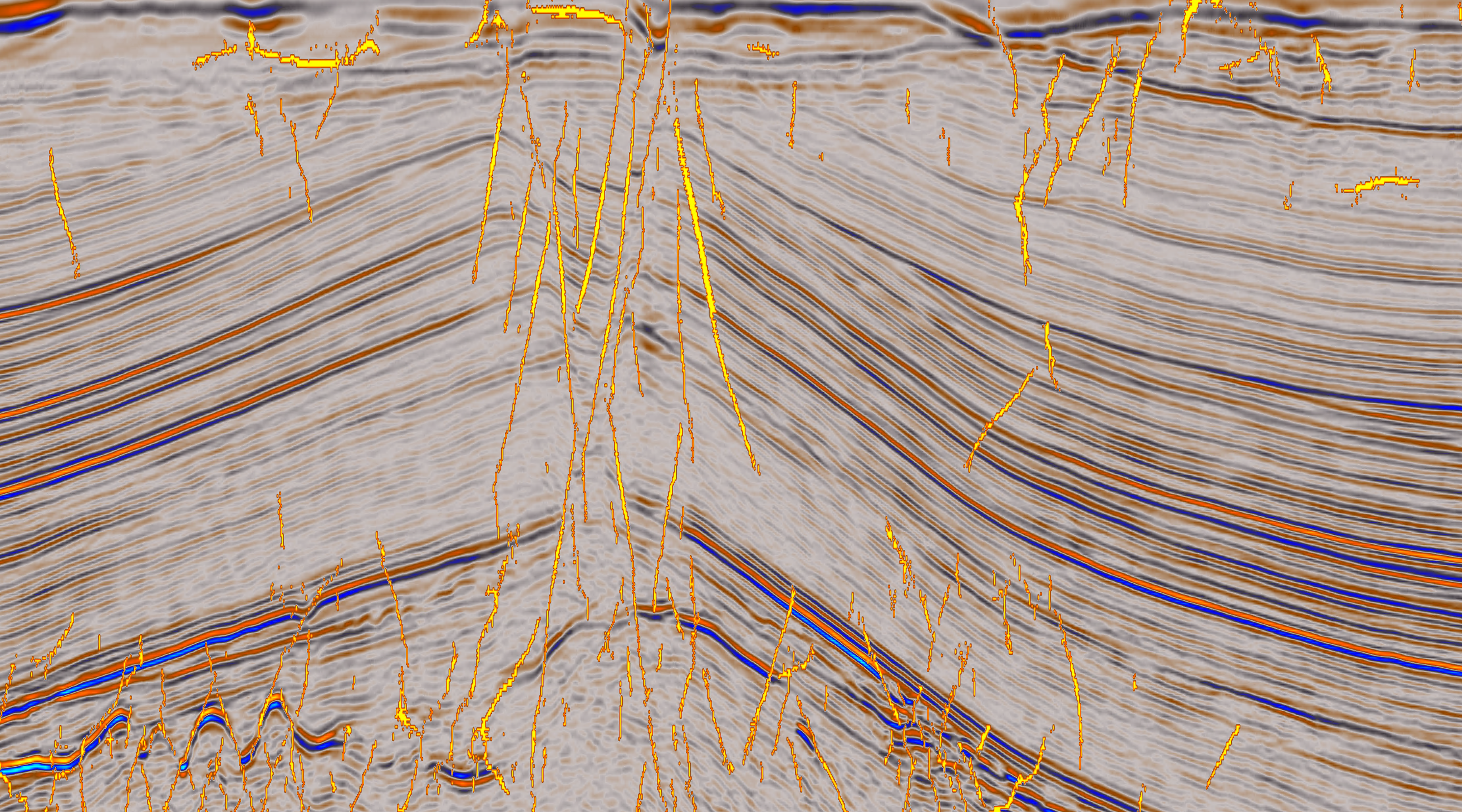
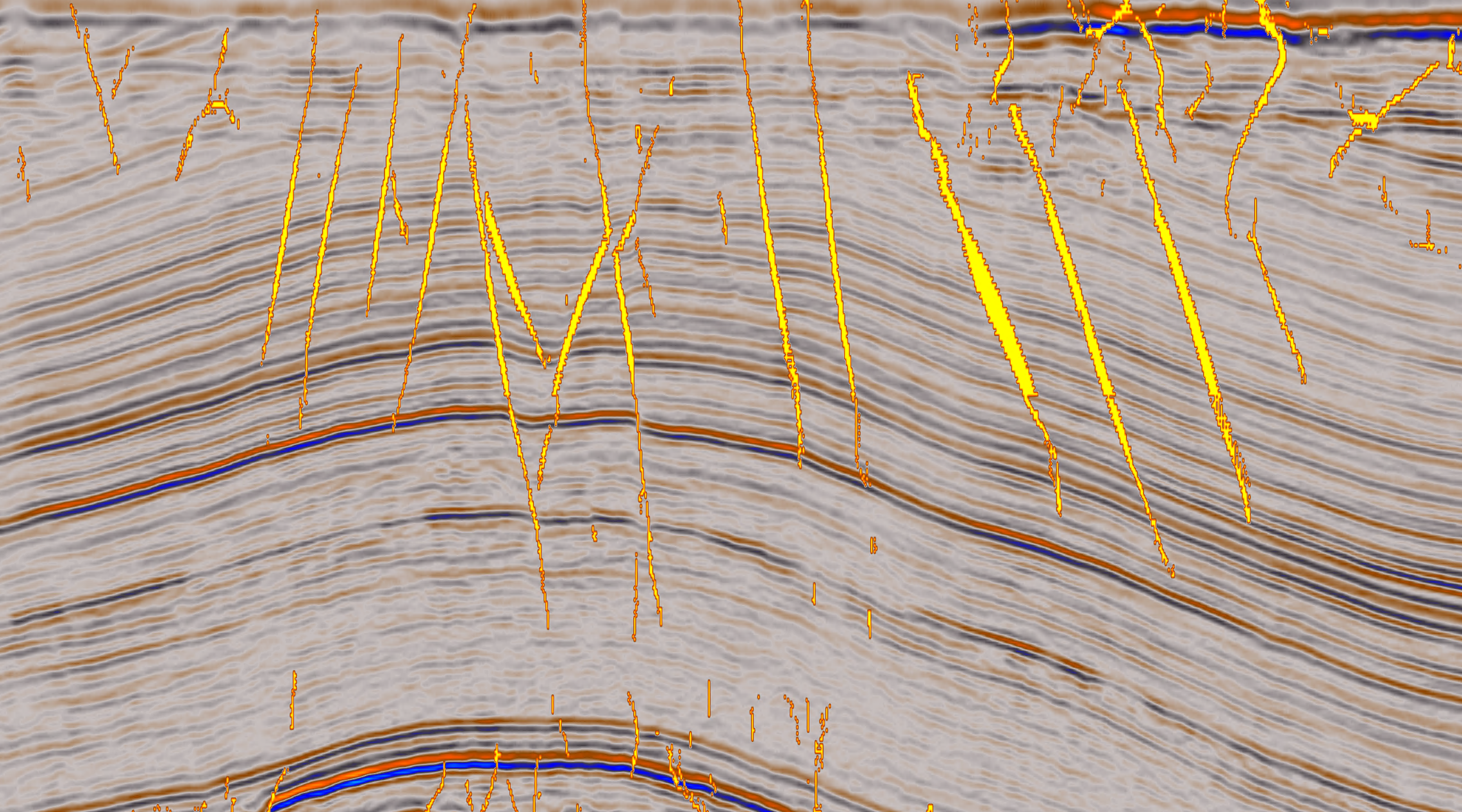

Combining artificial intelligence
Perth, Australia

Machine Learning Faults
Perth, Australia

AI software
Perth, Australia